在agnet中经常使用到bash命令调用,这里采用MCP stdio方式调。
1 使用Mcp Stdio方式-NewStdioMCPClient启动Stdio Server
在Stdio模式下,不需要启动Stdio server,直接使用 client.NewStdioMCPClient 即可
NewStdioMCPClient 用于创建一个通过 stdin/stdout 管道与子进程通信的 MCP 客户端,只是用来连接main文件的,不是类似sse/http streamable那种连接一个启动的server吧。执行流程如下:
- 启动一个新的子进程。执行对应的源文件 (go run main.go)或者 可执行文件。
- 通过 stdin/stdout 管道与子进程通信
- 子进程的 main 函数必须实现 MCP Server 的 stdio 监听
StartMcpStdioServer 其实就是为了定义一个main.go或者生成一个可执行文件,不需类似SSE、http streambel启动成一个服务。
整体方案:
- mcp_handler.StartMcpStdioServer()定义在其他一个main.go文件,只给NewStdioMCPClient调用使用
- 主main.go用来启动一个hertz服务
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
hertz-mcp-project/ ├── go.mod ├── go.sum ├── main.go # Hertz HTTP 服务的 main ├── cmd/ │ └── mcp-server/ │ └── main.go # MCP Stdio Server 的 main ├── handler/ │ └── bash_stdio_tools.go └── README.md |
1、主main.go
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
func main() { StartWithHertz() } func StartWithHertz() { h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8899")) h.GET("/execBash", handler.BashStdioTools) h.Spin() } |
2. handel/bash_stdio_tools 定义/execBash接口,通过NewStdioMCPClient执行
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
func BashStdioTools(ctx context.Context, cc *app.RequestContext) { command := cc.Query("command") result, err := ExecBashStdioTools(ctx, command) if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) cc.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{ "message": -1, "filename": err.Error(), }) return } cc.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{ "message": 0, "filename": result, }) return } func ExecBashStdioTools(ctx context.Context, command string) (string, error) { // 获取当前可执行文件路径 c, _ := client.NewStdioMCPClient("go", nil, "run", "/Users/bytedance/go/src/me/mcp_server/cmd/mcp_server/main.go") defer func() { // 捕获panic if r := recover(); r != nil { fmt.Println("Recovered from panic:", r) // 堆栈 fmt.Println("Stack trace:", r) } }() // Initialize initRequest := mcp.InitializeRequest{} initRequest.Params.ProtocolVersion = mcp.LATEST_PROTOCOL_VERSION initRequest.Params.ClientInfo = mcp.Implementation{ Name: "test-client", Version: "1.0.0", } result, err := c.Initialize(ctx, initRequest) if err != nil { errorInfo := fmt.Sprintf("Failed to initialize: %v", err.Error()) fmt.Println(errorInfo) return "", fmt.Errorf(errorInfo) } fmt.Println("InitializeRequest............") fmt.Printf("init result: %+v", result) // 调用 tool // 构建 tool call request request := mcp.CallToolRequest{ Params: mcp.CallToolParams{ Name: "BashExec", Arguments: map[string]interface{}{ "command": command, }, }, } callResult, err := c.CallTool(ctx, request) if err != nil { return "", fmt.Errorf("failed to call BashExec: %w", err) } // 提取返回内容 if len(callResult.Content) > 0 { if textContent, ok := callResult.Content[0].(mcp.TextContent); ok { return textContent.Text, nil } } return "", fmt.Errorf("no content returned from BashExec") } |
3、cmd/mcp-server/main.go 定义stdio server
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
func main() { mcp_handler.StartBashMcpStdioServer() } func StartBashMcpStdioServer() { // Create a new MCP server BashMcpServer := server.NewMCPServer( "BashDemo", "1.0.0", server.WithToolCapabilities(true), server.WithResourceCapabilities(true, true), ) // Add tool tool := mcp.NewTool("BashExec", mcp.WithDescription("执行bash命令并返回命令内容"), mcp.WithString("command", mcp.Required(), mcp.Description("要执行的bash命令"), ), ) // Add tool handler BashMcpServer.AddTool(tool, BashHandler) // Start the stdio server if err := server.ServeStdio(BashMcpServer); err != nil { fmt.Printf("Server error: %v\n", err) } } |
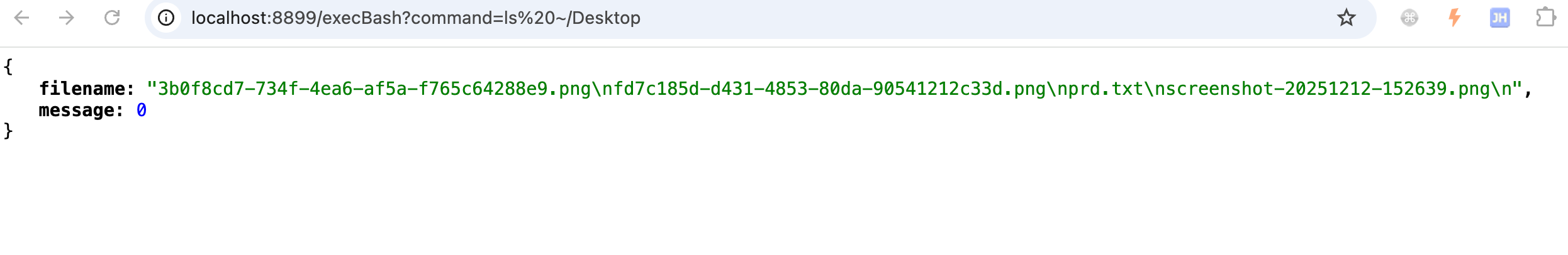
4、验证

2 构建Bash命令执行
1、 执行bash的工具类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
func ExecBash(ctx context.Context, command string) (string, error) { // 执行 bash 命令 cmd := exec.CommandContext(ctx, "bash", "-c", command) var stdout, stderr bytes.Buffer cmd.Stdout = &stdout cmd.Stderr = &stderr // 执行命令 err := cmd.Run() // 构建返回内容 var resultText strings.Builder // 添加标准输出 if stdout.Len() > 0 { resultText.WriteString(stdout.String()) } // 如果有错误,添加错误信息 if err != nil { if resultText.Len() > 0 { resultText.WriteString("\n") } resultText.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("Error: %v", err)) // 添加标准错误输出 if stderr.Len() > 0 { resultText.WriteString("\n") resultText.WriteString(stderr.String()) } } else if stderr.Len() > 0 { // 即使命令成功,也可能有 stderr 输出 if resultText.Len() > 0 { resultText.WriteString("\n") } resultText.WriteString("Stderr: ") resultText.WriteString(stderr.String()) } // 如果没有任何输出 if resultText.Len() == 0 { resultText.WriteString("Command executed successfully with no output") } return resultText.String(), nil } |
2. 修改上面的BashHandler:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
func BashHandler(ctx context.Context, request mcp.CallToolRequest) (*mcp.CallToolResult, error) { // 从请求中获取命令 command := request.GetArguments()["command"].(string) <strong>// 执行 bash 命令 result, err := ExecBash(ctx, command) if err != nil { return nil, err }</strong> return &mcp.CallToolResult{ Content: []mcp.Content{ mcp.TextContent{ Type: "text", Text: result, }, }, }, nil } |
3. 运行 ls ~/Desktop